Semantic Annotations
Contents
Semantic Annotations#
Semantic annotations refer to the process of adding metadata or labels to textual or multimedia content to provide additional contextual information and meaning. These annotations are used to enhance the understanding, organization, and retrieval of information by both humans and machines.
Semantic annotations can be applied at different levels, such as word or phrase level, document level, or even across multiple documents. The annotations may include various types of information, such as:
Entity Recognition: Identifying and labeling named entities in text, such as names of people, organizations, locations, dates, etc. This helps in extracting specific information and understanding the relationships between entities.
Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging: Assigning grammatical tags to each word in a sentence, indicating its role and function (e.g., noun, verb, adjective, etc.). POS tagging aids in syntactic analysis and understanding the grammatical structure of text.
Sentiment Analysis: Assigning sentiment labels (positive, negative, neutral) to text or parts of text to determine the overall sentiment expressed. This is useful in analyzing opinions, reviews, and social media sentiment.
Topic Modeling: Assigning topics or themes to documents or text segments based on their content. Topic modeling algorithms can automatically discover the main subjects or themes discussed in a collection of documents.
Relation Extraction: Identifying and labeling relationships between entities in text. For example, extracting relationships like “person A works for organization B” from a set of sentences.
Semantic annotations provide a way to make content more accessible, searchable, and interconnected. They enable advanced information retrieval techniques, such as faceted search, where users can filter and explore information based on different semantic criteria. Additionally, these annotations are essential for various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as information extraction, question answering, and text summarization.
The process of adding semantic annotations can be performed manually by human annotators or automated using machine learning techniques, such as named entity recognition (NER), sentiment analysis models, or topic modeling algorithms.
How to Annotate Akkadian Texts#
First, we will prepare one text as an example:
→ Go to ORACC/SAAo/SAAo5
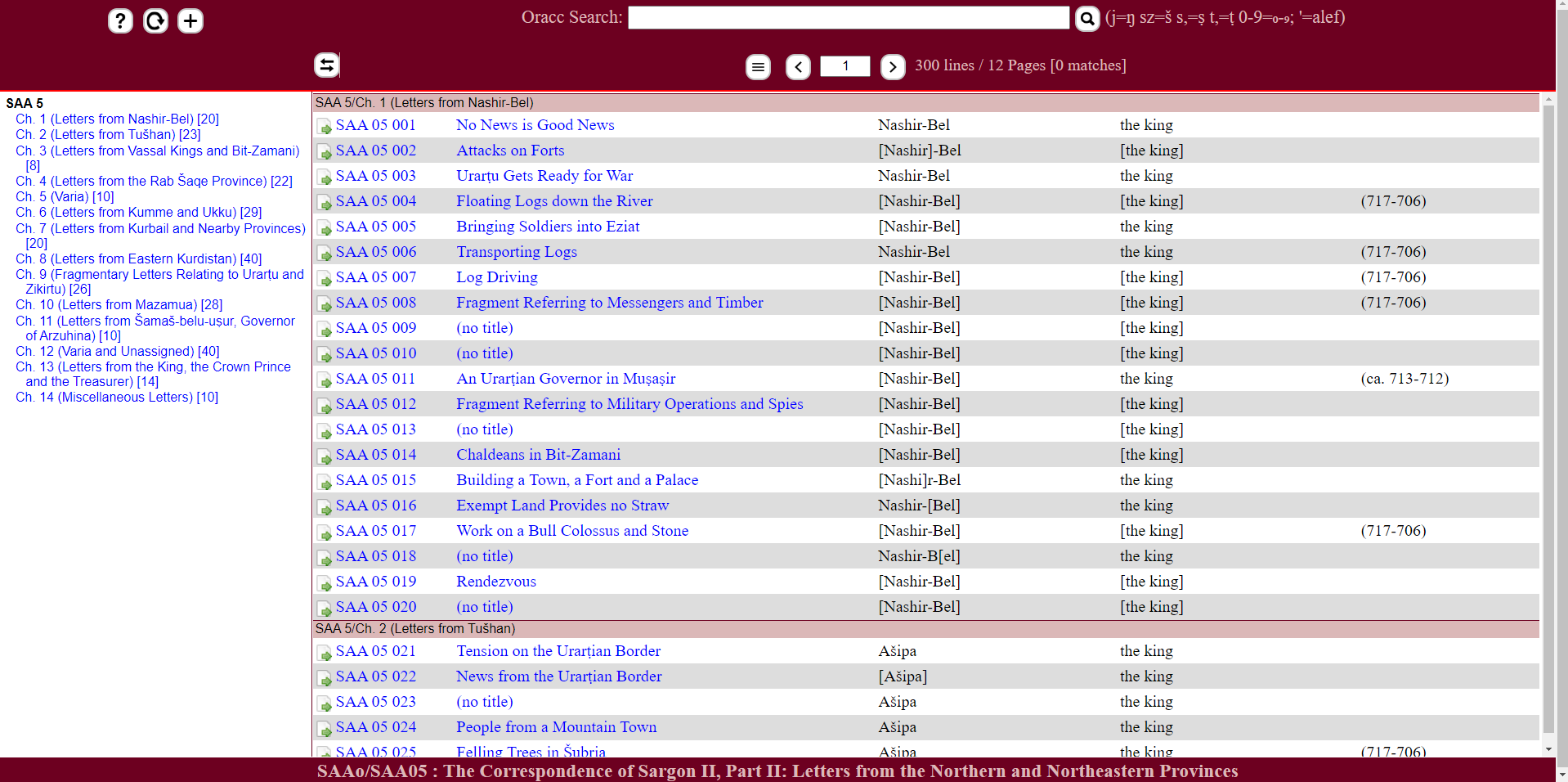
Fig. 3 Browse SAAo 5.#
→ Select the transliteration and translation and then copy and paste it in your Quelltext-Editor, e.g. SAA 5, 001.
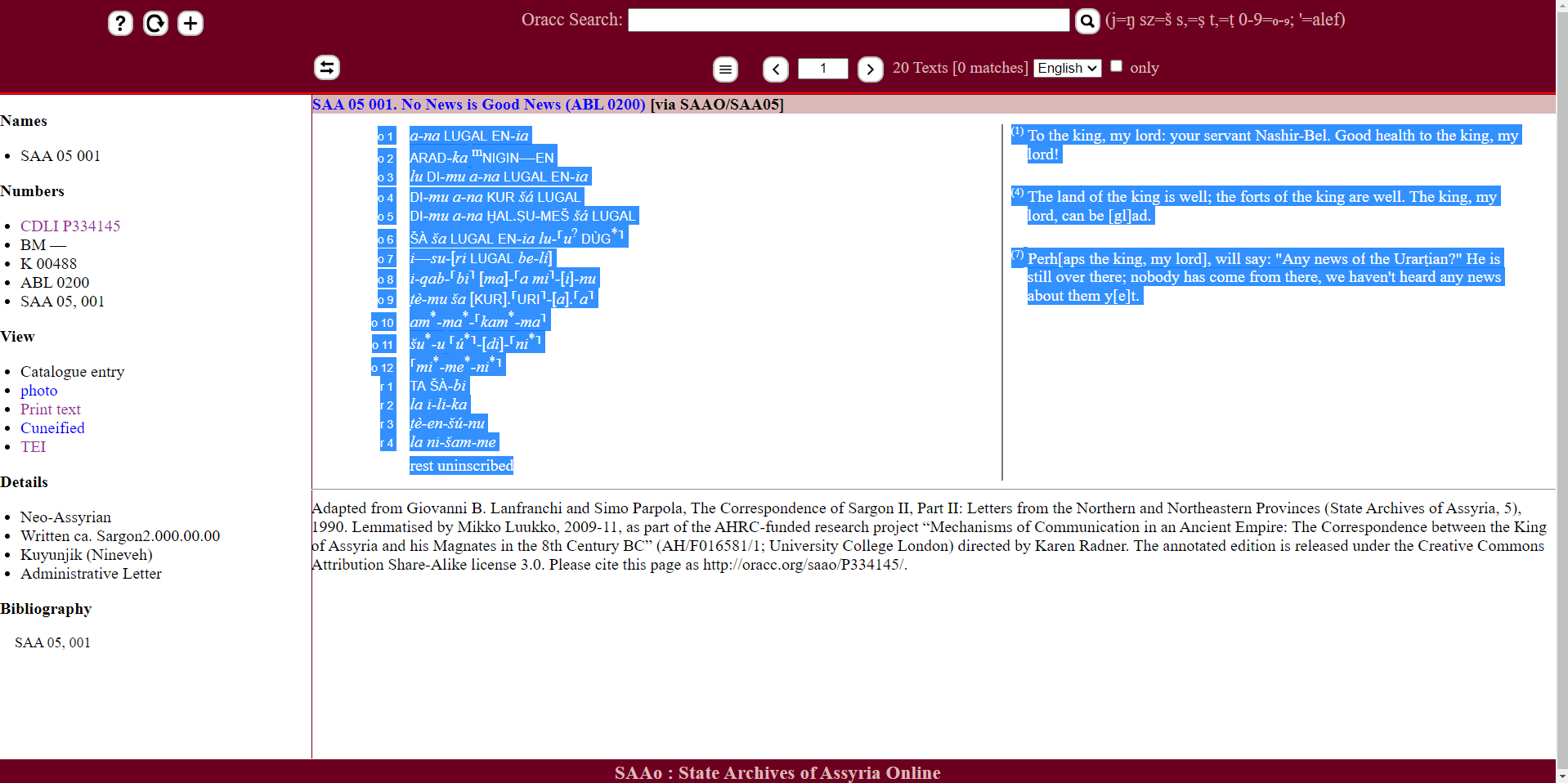
Fig. 4 Selected text of SAAo 5 001.#
Note
There are many ways to download it. We could download the whole SAA 05 or even SAA. You can follow the instruction in Compass, the Jupyter Notebook of Niek Veldlhuis, for downloading the whole SAA corpus and cleaning the data for the purposes you need.
→ Prepare the Akkadian text and the translation as follow using RegEx:

Fig. 5 Cleaned translitearation and translation of SAAo 5 001.#
→ Save the normalized text and the translation as two different text files.
For the annotations, we use INCEpTION.
This is a powerful and flexible annotation platform that assists researchers and practitioners in efficiently annotating and preparing text data for training and evaluating NLP models. This annotation tool offers support for machine learning models integration, allowing users to train and improve NLP models using the annotated data.
→ Open the text file in INCEpTION and make the annotations you want. You can add many layers of annotations.
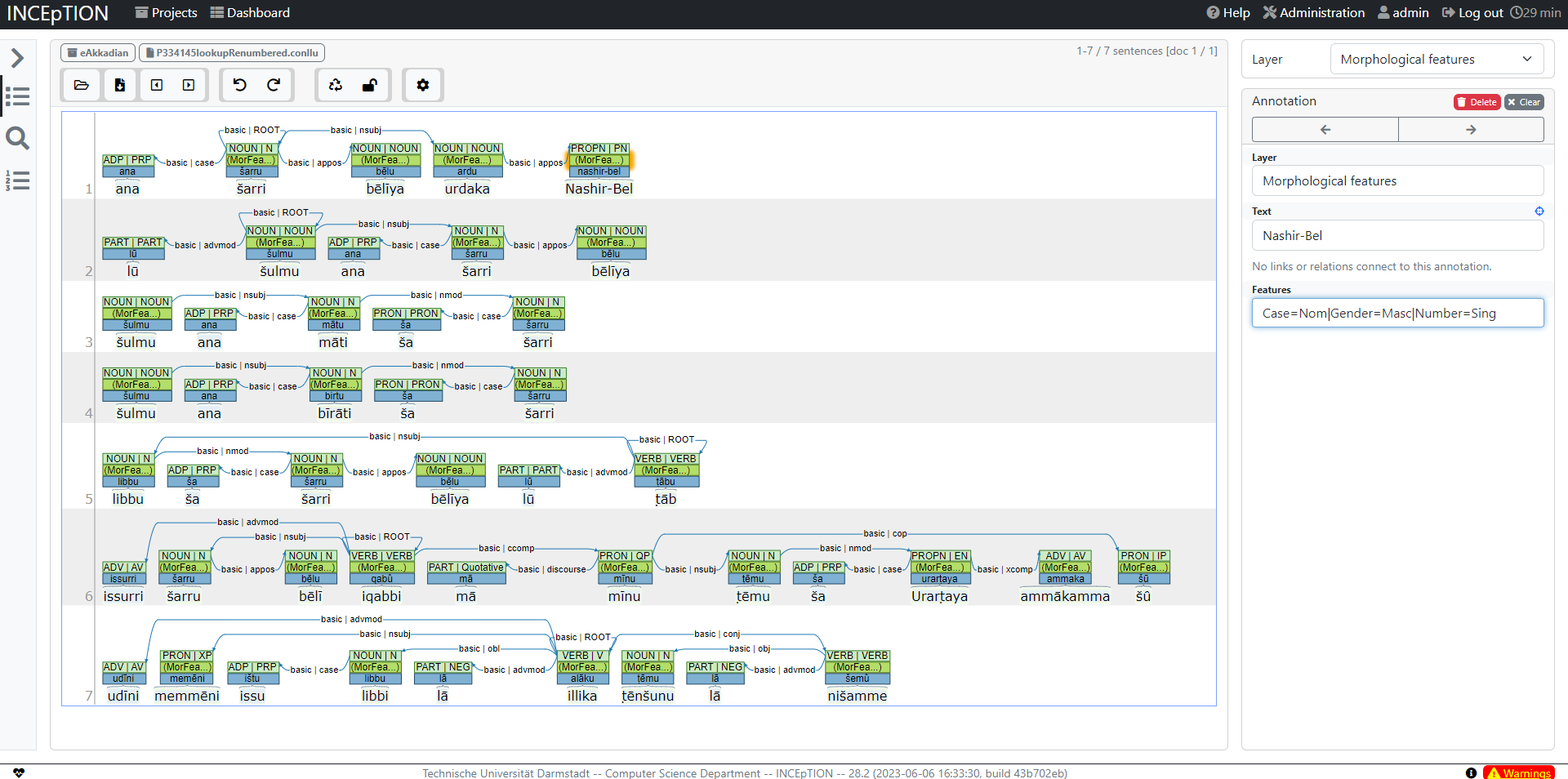
Fig. 6 Annotated Akkadian text in INCEpTION.#
In this way you can have a close reading of an Akkadian text and understand the syntactic relationship within a sentence. This data can be later used for NLP tasks. An article on this topic by Matthew Ong and Shai Gordin is being reviewed.
